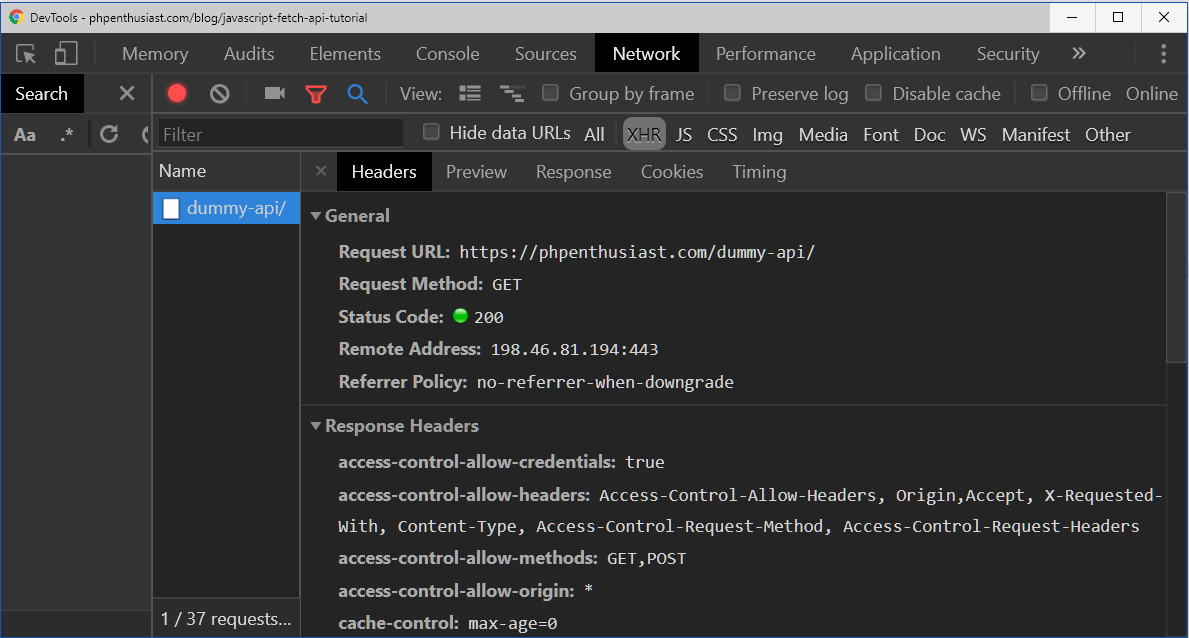
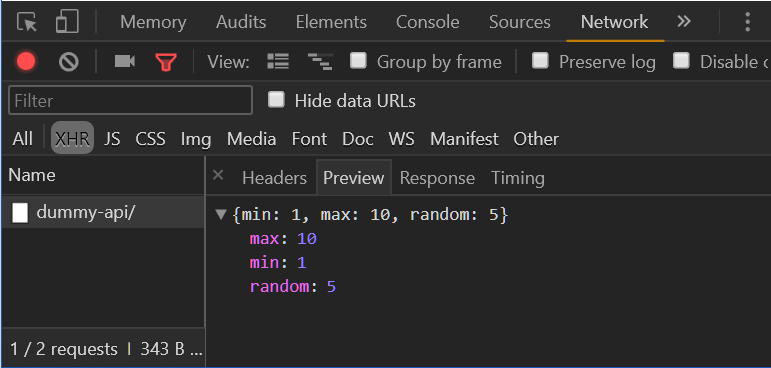
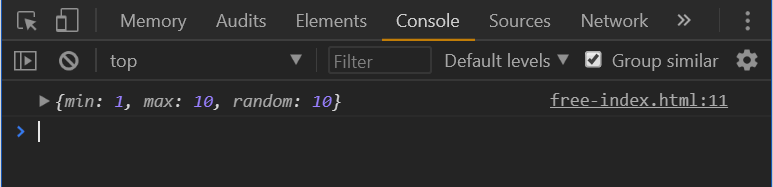
# 2. Posting data with the Fetch
To post the data to the server, you need to add a JSON object as the second parameter that you pass to the fetch() method:
fetch('https://phpenthusiast.com/dummy-api/', {
method : 'post'
})
.then((res) => res.json())
.then((data) => console.log(data))
.catch((error) => console.log(error))
Except for the "method" field, you also need to provide the "body" field with the actual data that you want to send to the server:
fetch('https://phpenthusiast.com/dummy-api/', {
method : 'post',
body: JSON.stringify({min: 1, max: 100})
})
.then((res) => res.json())
.then((data) => console.log(data))
.catch((error) => console.log(error))
You need to use the JSON.stringify() method to make a string out of the data because you can't send objects.
The fields "mode" and "headers" are not essentials, yet you need to know about them:
fetch('https://phpenthusiast.com/dummy-api/', {
method : 'post',
mode: 'cors',
headers: {
'Content-Type': 'application/json', // sent request
'Accept': 'application/json' // expected data sent back
},
body: JSON.stringify({min: 1, max: 100})
})
.then((res) => res.json())
.then((data) => console.log(data))
.catch((error) => console.log(error))
- The headers field specifies the data type for the sent data (Content-Type) as well as the received data (Accept).
The default value for the "mode" field is "cors" which allows it to send requests to a different website from the one that sends the request. For example, send requests to Facebook, Google, or other API providers.
Another condition is that the service provider needs to configure the server to allow data exchange with external apps.
If the API provider doesn't configure the server, you can use the "no-cors" option, which will allow the sending of data to the server, but without getting a response back.
The "same-origin" option requires the request to be on the same server.